Should You Adopt AI in Your OB-GYN Practice?
With the buzz around Artificial Intelligence (AI), it is understandable that you may be wondering how it can help or hinder your OB-GYN practice. AI has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of healthcare, offering innovative solutions that could enhance diagnostics, streamline processes, and improve patient outcomes.
However, integrating AI into your OB-GYN practice requires careful consideration, as it comes with challenges and ethical considerations.
In this article, we will explore the increasing role of AI in healthcare, specifically in OB-GYN practices, and consider whether integrating AI aligns with the values and goals of such practices.
The Rise of AI in Healthcare
The healthcare landscape is undergoing a transformative shift with new technologies and the integration of AI. According to recent expenditure statistics, implementing AI technologies has witnessed a significant uptrend, particularly in data analysis and decision support systems.
As the potential applications of AI become more apparent, OB-GYN practices are exploring how this cutting-edge technology can contribute to enhanced patient care and diagnostics.
AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data swiftly and accurately presents a promising avenue for revolutionizing the traditional approaches in OB-GYN healthcare.
This surge in interest reflects the industry’s recognition of AI as a potential catalyst for improving efficiency, accuracy, and overall healthcare outcomes.
Should You Adopt AI in Your OB-GYN Practice?
As healthcare evolves, the question remains: should you adopt AI in your OB-GYN practice?
While hesitations persist within the medical community, viewing AI as an opportunity for progress rather than a cause for concern is essential. By leveraging advanced technologies like OB-GYN EHR software, OB-GYN practitioners can stay at the forefront of healthcare, providing personalized and effective care for women.
AI has the potential to revolutionize disease management, deepen our understanding of women’s health conditions, and elevate the quality of care provided.
While some applications are still in their infancy and not without imperfections, AI in this context is not something to fear. Rather, it represents an opportunity for the medical community to catch up with the evolving landscape of technology and provide more personalized and effective care for conditions impacting women.
As research in this field progresses, embracing AI may significantly improve patient outcomes and contribute to the advancement of women’s healthcare.
AI Use Cases for OB-GYN Practices
AI holds promise in various applications in obstetrics and gynecology, although extensive research and refinement are still underway.
With many potential uses on the rise, note that not all are available to implement into your practice right away.
Explore the chart below to consider your best options, including an estimate of when this technology is likely to become more acceptable in clinical practice.
AI Technology | Use Case | Date of Potential Adoption |
Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring (cardiotocography) | Improved efficacy in early fetal diagnostics, potentially birth asphyxia | 2025 |
Data-based patient record screening for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus | Advanced screening for multiple patients, including multiple risk factors and early analysis | 2024 |
Predicting Potential Preterm Labor | Fast and data-driven insights around preterm labor characteristics for improved healthcare outcomes | 2025 |
Improved Results for In Vitro Fertilization | AI applications in gamete selection, embryo selection, and treatment programs | 2026+ |
Cancer Screening | Algorithms and data analysis to identify potential gynecological cancers early | 2025 |
Assisting in Gynecological Surgeries | 3D and AR surgery for improved surgical planning and real-time support | 2024 |
Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring
AI shows promise in significantly improving fetal heart rate monitoring, providing more accurate and real-time assessments during pregnancy based on AI’s ability to interpret images (see Aeberhard et al., 2024).
This technology can analyze complex patterns and deviations, offering valuable insights that may assist healthcare practitioners in making timely and informed decisions.
Image: Pipeline of machine learning for cardiotocography (O’Sullivan, 2021).
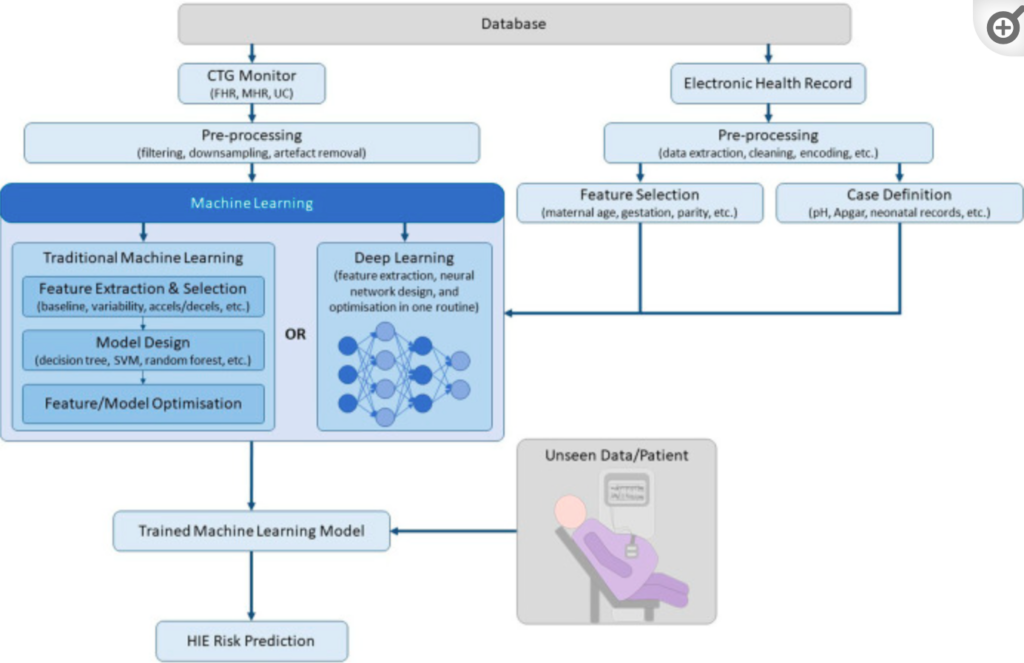
While advancements in AI-driven fetal heart rate monitoring are noteworthy, it is essential to acknowledge that further research and refinement are needed to ensure the technology’s reliability and safety in diverse clinical settings. Right now, this technology is still in the data collection phase; however, collecting data in clinics is a possibility.
The integration of AI in this context reflects an exciting frontier that could revolutionize prenatal care, but careful consideration and ongoing study are crucial for its widespread adoption.
Screening for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Screening for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a critical aspect of prenatal care, and AI applications have shown promise in improving this process.
AI can improve GDM screenings with advanced algorithms for more precise diagnostics, as is indicated by early research using MIDO GDM. MIDO GDM used machine learning to parse through patient data and pull out potential indicators of GDM.
Image: Overview of MIDO GDM processing for GDM screening (Gallardo-Rincon et al., 2023).
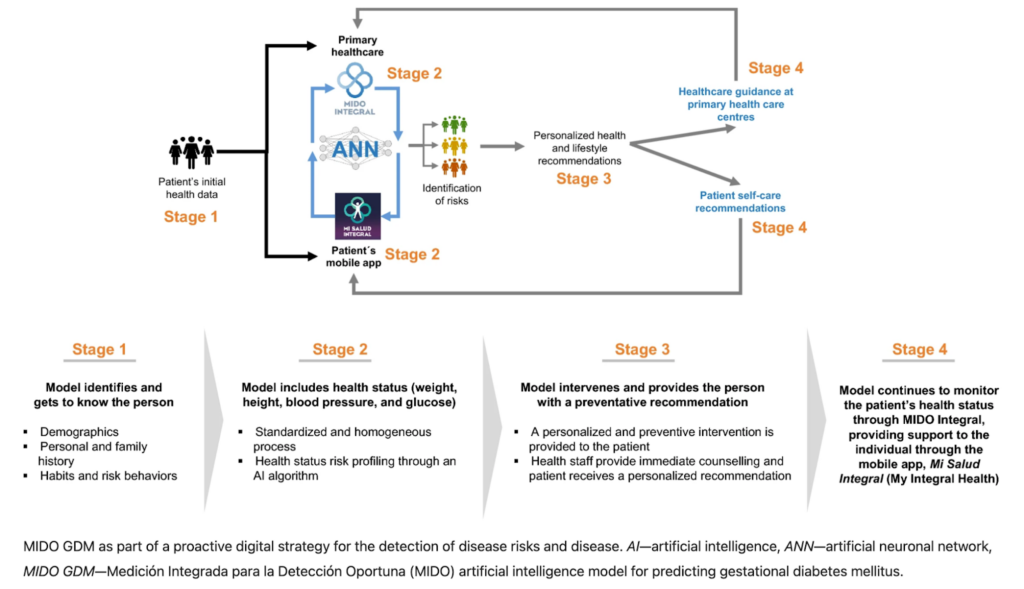
This not only streamlines the screening workflow but also contributes to early detection and intervention, ultimately benefiting both the mother and the baby.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, embracing machine learning models in gestational diabetes screening may become a valuable strategy for OB-GYN practices aiming to elevate the standard of care for pregnant individuals.
Predicting Potential Preterm Labor
Preterm labor is a significant concern in obstetrics, and AI algorithms offer a promising avenue for predicting and managing this risk.
By analyzing various factors and patterns, these algorithms can provide valuable insights into the likelihood of preterm labor, empowering healthcare providers to implement timely interventions.
According to researchers of one study who analyzed AI efficacy in determining preterm labor:
“We predicted the pregnancies’ outcomes from EHG recordings using a deep neural network, because neural networks automatically learn the most informative features from the data,” Goldsztejn said. “The deep learning algorithm achieved a better performance than other methods and provided a good way to combine EHG data with clinical information.”
This capability aligns with the broader goal of personalized and proactive maternal care, ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Image: Clinical process adaptation of machine learning in preterm labor (Goldsztejn & Nehorai, 2023)
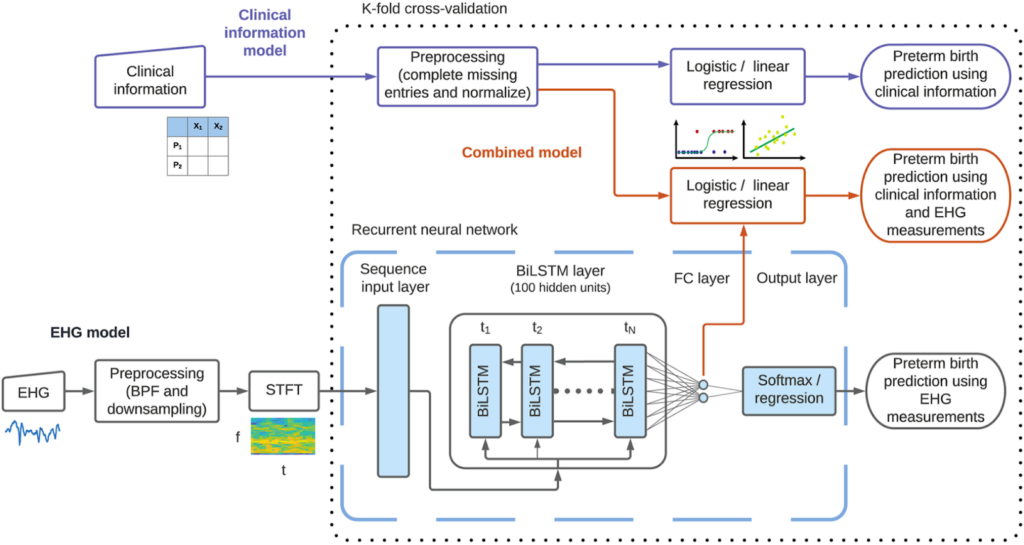
As research and technology advance, incorporating AI into preterm labor prediction may become crucial for OB-GYN practices seeking to enhance patient outcomes.
Improved Results for In Vitro Fertilization
AI’s role in fertility treatments, particularly In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), offers a promising avenue for optimizing success rates.
Image: Emerging role of AI in vitro fertilization success rates (Chow et al., 2021)
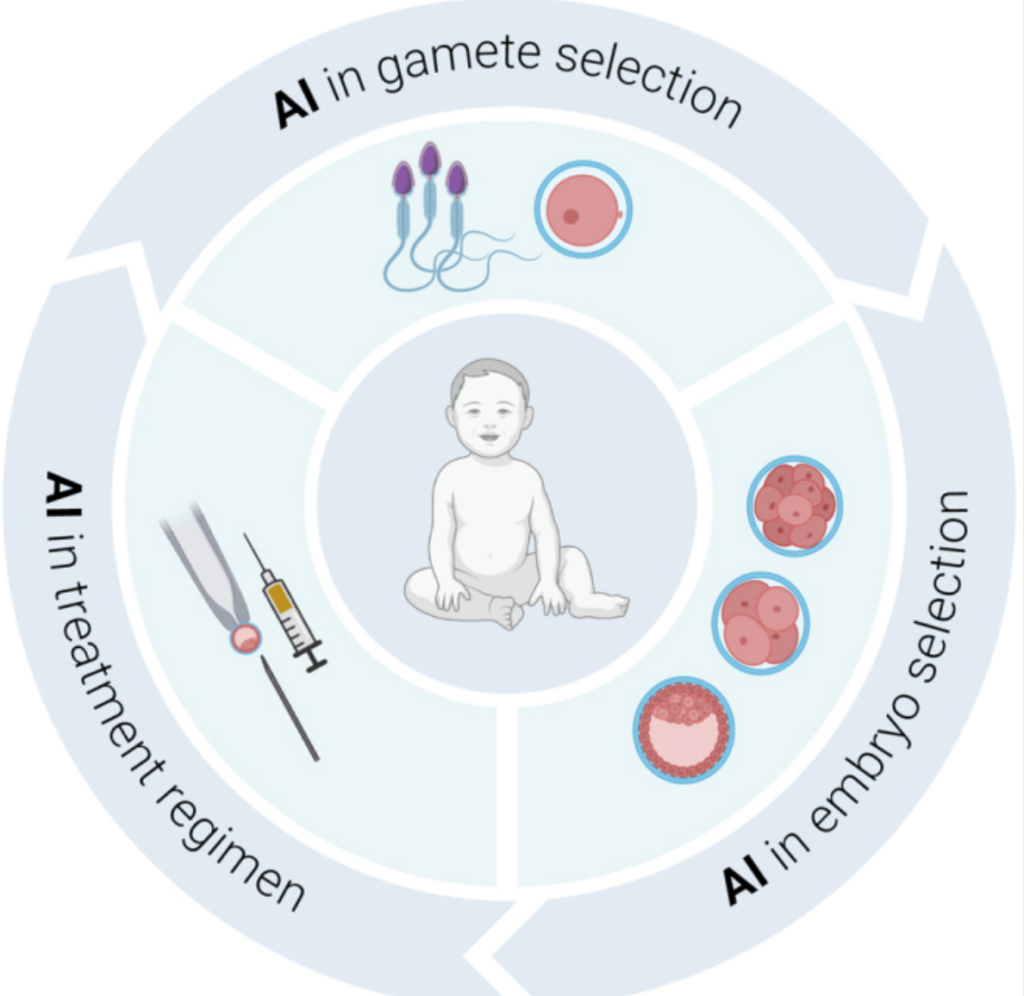
AI can analyze various factors influencing IVF outcomes through advanced algorithms and data analysis, contributing to more precise decision-making.
It’s important to recognize the steps needed for IVF clinics to adopt this widespread:
Table: Derived from Chow et al., (2021).
Steps Needed To Implement AI in IVF Clinics | |
Hurdles | Requirements to develop IA in infertility services |
Clinics are too small and don’t usually produce enough data for AI to use. | Collaboration to develop standardized procedures for recording and reporting patient data. |
There is limited computing power and data storage. | Multi-clinic processes for sharing anonymized patient data. |
Challenges with discrepancies in recorded patient characteristics and outcomes between clinics exist. | Increased computing power, data storage and technology security funding. |
Variations in study input parameters alter the predictive outcomes. | Consensus on input parameters for AI outcomes. |
Rigorous, high-quality peer-reviewed validation for AI algorithms. | |
This application of AI reflects the evolving landscape of reproductive medicine, potentially boosting the effectiveness of IVF procedures.
Cancer Screening
AI use cases in cervical cancer screening have been heavily researched (see Hou et al., 2022; and Vargas-Cardano, 2023).
Integrating AI into cancer screening practices within obstetrics and gynecology signifies a transformative leap in early detection methods.
Image: Classification of machine learning algorithms according to a scoping review (Vargas-Cardano, 2023).
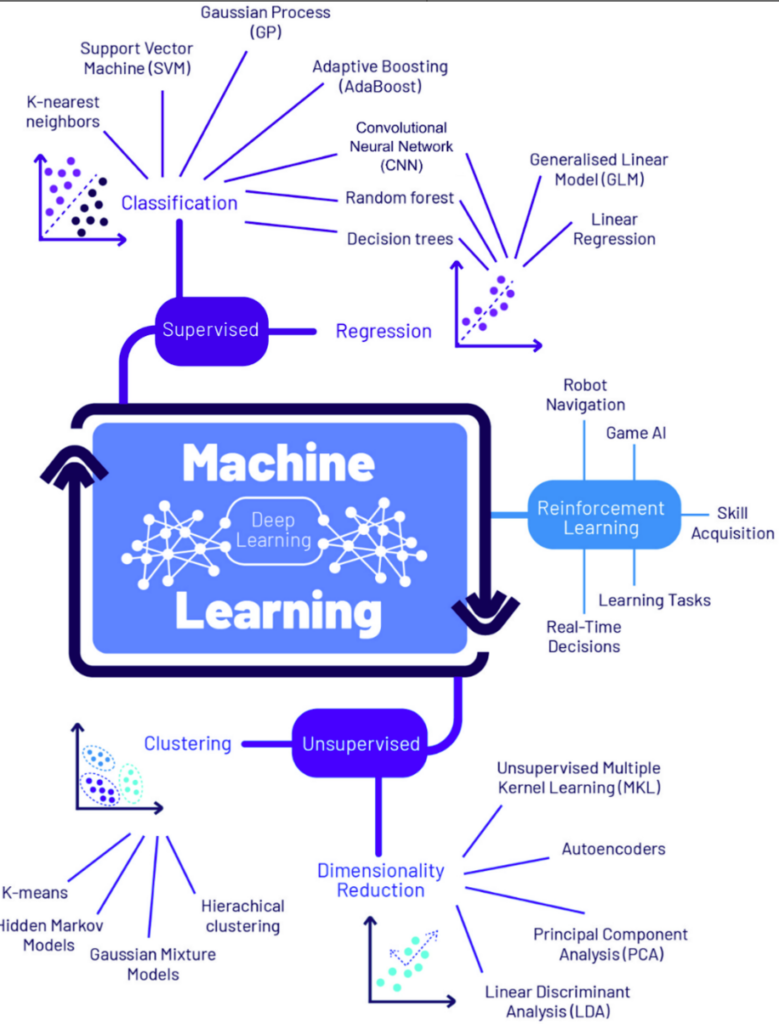
Advanced algorithms and data analysis, critical components of AI, empower healthcare professionals to identify potential gynecological cancers early, improving patient outcomes and providing more effective treatment strategies.
Assisting in Gynecological Surgeries
Gynecological surgeries benefit from improved precision, reduced complications, and enhanced overall outcomes by harnessing AI’s capabilities.
Integrating AI technologies into surgical procedures allows for real-time data analysis and decision support, providing surgeons with valuable insights.
Uses of augmented reality and AI in gynecological surgeries include:
- 3D and AR mapping of the surgical area
- Advanced imaging to avoid unnecessary surgeries
- Minimized risks during surgical procedures
- Advancement of AI-related surgical tools
- Real-time guidance during surgery
As AI continues to evolve, its role in gynecological surgeries showcases the potential for advancements in surgical techniques, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes in obstetrics and gynecology.
Embracing AI in Your OB-GYN Practice with DigiChart
The rise of Artificial Intelligence in healthcare signals a transformative era for OB-GYN practices. From fetal heart rate monitoring to predicting preterm labor and refining cancer screenings, the potential applications of AI are vast and promising.
Although some areas require further research, the overall trajectory points towards enhanced diagnostics, improved patient outcomes, and a deeper understanding of women’s health conditions.
To explore how our innovative technologies can elevate your OB-GYN practice into the future of healthcare.
FAQs Related to AI in OBGYN Clinics
What is the role of AI in obstetrics and gynecology?
AI can significantly enhance obstetrics and gynecology by improving diagnostic accuracy, optimizing patient care, and advancing treatment outcomes.
Key areas where AI shows promise include fetal heart rate monitoring, screening for gestational diabetes, predicting preterm labor, assisting in vitro fertilization (IVF) success rates, facilitating early cancer detection, and supporting gynecological surgeries.
What are the pros and cons of implementing AI in healthcare?
AI can process vast amounts of data swiftly, enhancing diagnostic precision and streamlining workflows. AI’s data analysis capabilities enable more tailored treatment plans, aligning closely with individual patient needs and improving patient care.
Incorporating AI into existing healthcare systems can be complex, requiring significant investment in technology and training. AI’s effectiveness is contingent upon the availability of large, high-quality datasets, which may not always be accessible or standardized across different healthcare settings.
What are the limitations of AI in healthcare?
Several factors, including the quality and quantity of data available for training algorithms, the potential for biases in AI models, and the need for substantial investment in technology infrastructure limit AI in healthcare.
Additionally, AI cannot replace the nuanced judgment and empathetic care provided by human healthcare professionals, which are crucial in patient-centered care.
Ethical and regulatory considerations also pose significant constraints, necessitating careful oversight to ensure patient privacy and equity in healthcare delivery.
What are the risks with AI in healthcare?
The primary risks associated with AI in healthcare include potential data privacy breaches, the amplification of existing biases in medical treatment, and the reliance on algorithms that may not always account for the complexity of individual patient cases.
There’s also the risk of over-reliance on AI, which could potentially devalue the critical role of human judgment and the patient-doctor relationship in healthcare.
Ensuring the ethical use of AI, maintaining rigorous standards for data security, and fostering a balanced integration of AI with human oversight are essential to mitigate these risks.
References
O’Sullivan,M. E., Considine, E. C., O’Riordan, M., Marnane, W. P., Rennie, J. M., & Boylan, G. B. (2021). Challenges of developing robust AI for intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 4, 765210. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8576107/
Aeberhard, J. L., Radan, A. P., Soltani, R. A., Strahm, K. M., Schneider, S., Carrié, A., … & Surbek, D. (2024). Introducing Artificial Intelligence in Interpretation of Foetal Cardiotocography: Medical Dataset Curation and Preliminary Coding—An Interdisciplinary Project. Methods and protocols, 7(1), 5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10801612/
Gallardo-Rincón, H., Ríos-Blancas, M. J., Ortega-Montiel, J., Montoya, A., Martinez-Juarez, L. A., Lomelín-Gascón, J., … & Tapia-Conyer, R. (2023). MIDO GDM: an innovative artificial intelligence-based prediction model for the development of gestational diabetes in Mexican women. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 6992. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-34126-7
Zhang, Z., Yang, L., Han, W., Wu, Y., Zhang, L., Gao, C., … & Wu, H. (2022). Machine learning prediction models for gestational diabetes mellitus: meta-analysis. Journal of medical Internet research, 24(3), e26634. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8968560/
Suman, V., & Luther, E. E. (2019). Preterm labor. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536939/
Neuroscience News. (May 30, 2023). “AI Can Predict Preterm Birth at 31 Weeks of Gestation”. https://neurosciencenews.com/ai-preterm-birth-23371/
Goldsztejn, U., & Nehorai, A. (2023). Predicting preterm births from electrohysterogram recordings via deep learning. Plos one, 18(5), e0285219. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285219
Chow, D. J., Wijesinghe, P., Dholakia, K., & Dunning, K. R. (2021). Does artificial intelligence have a role in the IVF clinic?. Reproduction and Fertility, 2(3), C29-C34. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8801019/
Vargas‐Cardona, H. D., Rodriguez‐Lopez, M., Arrivillaga, M., Vergara‐Sanchez, C., García‐Cifuentes, J. P., Bermúdez, P. C., & Jaramillo‐Botero, A. (2023). Artificial intelligence for cervical cancer screening: Scoping review, 2009–2022. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37811597/
Hou, X., Shen, G., Zhou, L., Li, Y., Wang, T., & Ma, X. (2022). Artificial intelligence in cervical cancer screening and diagnosis. Frontiers in oncology, 12, 851367. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8963491/
Vargas‐Cardona, H. D., Rodriguez‐Lopez, M., Arrivillaga, M., Vergara‐Sanchez, C., García‐Cifuentes, J. P., Bermúdez, P. C., & Jaramillo‐Botero, A. (2023). Artificial intelligence for cervical cancer screening: Scoping review, 2009–2022. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ijgo.15179
Moawad, G., Tyan, P., & Louie, M. (2019). Artificial intelligence and augmented reality in gynecology. Current Opinion in Obstetrics and Gynecology, 31(5), 345-348. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31259843/





